Have you ever looked at an electrical outlet and wondered about the different wires lurking within? It’s a question that’s crossed the minds of many, especially those who aren’t well-versed in the intricate world of electricity. We often hear about “hot wires” and “load wires” but do we truly understand the difference? And more importantly, what are the implications of each when it comes to the safety and functionality of our electrical systems?
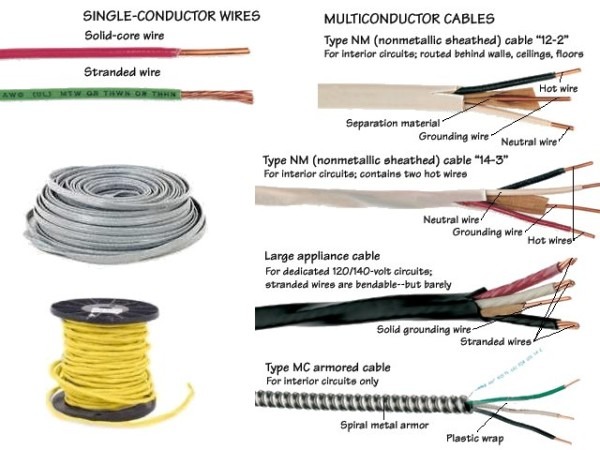
Image: www.chanish.org
This article will delve into the fascinating world of load and hot wires, shedding light on their essential roles and debunking common misconceptions. We’ll explore the historical context, the fundamental principles behind them, and uncover the practical implications for your everyday life. Buckle up as we embark on a journey of electrical enlightenment.
Understanding the Fundamentals: A Journey into Electrical Basics
Before dissecting the differences between load and hot wires, let’s establish a common understanding of the fundamental elements that shape the flow of electricity. Think of electricity like a river. Just as water flows downstream, electricity travels along a specific path called a “circuit”. This circuit typically consists of several key components:
- Source: This is where the electricity is generated, analogous to the headwaters of a river. Examples include power plants and batteries.
- Load: This represents anything that consumes electrical energy, like a light bulb, appliance, or device. It’s the “destination” where the electricity is used.
- Circuit Conductive Paths: These are the wires that provide the pathway for electricity to travel from the source to the load. They’re similar to the riverbed, guiding the water flow.
Now, within these conductive paths, a specific terminology is used to describe the different roles of wires:
- Hot Wire (aka Live Wire): This wire carries the electrical current, also known as voltage, from the source to the device. It’s the live, energized portion of the circuit.
- Neutral Wire: This wire serves as the return path for the electrical current back to the source. It completes the circuit and ensures that the current can flow freely.
- Ground Wire (aka Earth Wire): This wire is a safety feature designed to provide a pathway for electricity to safely flow to the earth in case of a fault or short circuit. It helps prevent electric shocks and protect equipment.
Dissecting the Differences: Load Wire and Hot Wire
The terms “load wire” and “hot wire” are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion. It’s crucial to understand the subtle differences:
- Hot Wire: As explained earlier, this is the wire carrying the electrical current from the source to the load, making it the “live” wire.
- Load Wire: While not a universally used term in the electrical industry, the load wire typically refers to the wire that carries the current to the load device. In many situations, it’s essentially the same as the hot wire.
So, how does this work? Imagine turning on a light switch. When you flip the switch, you are essentially completing a circuit. The hot wire (also often the load wire in this scenario) carries the electric current from the source (power outlet) to the light bulb, which acts as the load. The neutral wire carries the current back to the outlet, completing the circuit and allowing the light to illuminate.
Navigating the Real World: Practical Implications for Everyday Life
Understanding the roles of load and hot wires is not just a theoretical exercise. It has practical implications for your safety and the functionality of your electrical systems. Here are some key points to consider:
- Safety First: Always treat all wires in an electrical system as potentially dangerous, even if they are not “hot.” Improper handling can lead to electric shocks or damage to equipment.
- Wiring Installation: It’s essential that electrical wiring is installed by qualified electricians who adhere to safety standards and building codes. This ensures that the wires are correctly connected and that the circuit is balanced for optimal performance.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Understanding the different types of wires can help you identify potential problems in your electrical system. For instance, if you notice a disconnected or damaged load wire, you can diagnose the issue and take appropriate action.
Image: metersuk.co.uk
Expert Insights: Navigating the Electrical Maze
Here are some insights from experienced electricians and electrical engineers:
- Avoid DIY Electrical Work: Unless you are a licensed electrician, it’s best to leave electrical work to the professionals. Working with electricity can be dangerous if not done correctly.
- Regular Inspections: Have your electrical system inspected regularly by a licensed electrician. This can help prevent potential hazards, such as faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, or malfunctioning appliances, that could lead to fires or other serious incidents.
Load Wire Vs Hot Wire
Concluding Thoughts: Empowering Your Electrical Knowledge
Understanding the roles of hot wires, load wires, and other components is crucial for navigating the world of electricity safely. By embracing knowledge, you can become a more informed consumer and ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical systems. Remember, electricity is a powerful force, and it should always be treated with respect. If you are ever unsure about anything related to electricity, consult a licensed electrician for guidance and peace of mind.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




