Have you ever stared at a vibrant sunset and wondered how the colors seem to pulse with life? Or perhaps you’ve felt drawn to a richly saturated painting, mesmerized by its depth and intensity? The answer lies in a fundamental aspect of color theory: saturation. It’s the key that unlocks the vibrancy and richness of our visual world.
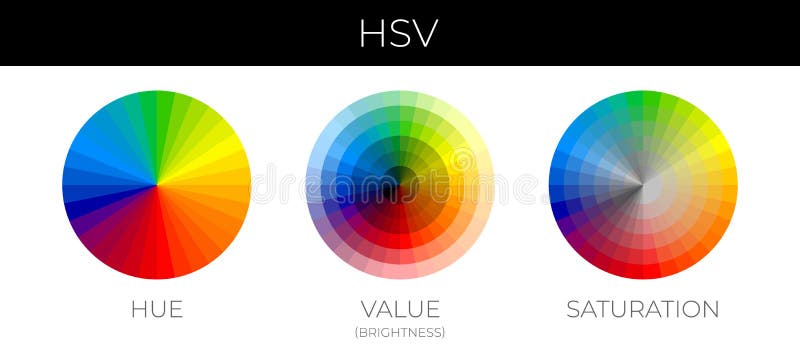
Image: www.vrogue.co
Saturation is, quite simply, the purity of a color. It’s the measure of how much of a particular color is present in a hue, a concept often described as the vividness, intensity, or chroma of a color. Imagine a spectrum of red: a bright, bold red is highly saturated, while a pale, washed-out red is low in saturation. Understanding saturation is crucial for anyone working with color, whether you’re an artist, a designer, a photographer, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of the world around you.
From the Basics to the Spectrum: Unveiling the Essence of Saturation
The Color Wheel and Saturation’s Role
To grasp saturation’s definition, let’s consider the color wheel, the bedrock of color theory. It presents a visual arrangement of pure hues, each representing a fundamental color. Imagine a pie chart divided into sections, each representing a pure hue. Moving outwards from the center of the pie, we encounter a gradual increase in saturation, beginning from a near-white center (low saturation) towards the edges (high saturation) where the pure hues reign. This movement reveals that saturation dictates the strength of the color, determining how vivid and vibrant it appears.
The RGB and CMYK Models: Understanding Color Systems
Color models are frameworks that help us understand and represent colors in different ways. Two prevalent models are RGB (Red, Green, Blue) and CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black). In the RGB model, often used for digital screens, saturation is measured by the percentage of red, green, and blue present in a color. The higher the percentage of a particular color, the higher its saturation.
CMYK, often used for printing, employs a different approach. In this model, saturation is determined by the proportions of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black used to create a color. For instance, a pure cyan color has high saturation because it consists of only cyan without black. The addition of black decreases the saturation, resulting in a less vivid color.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Exploring the Impact of Saturation: From Nature to Art
Nature’s Palette: Saturation in the Natural World
Nature is a master of color, demonstrating the power of saturation in countless ways. Look at ripe strawberries, bursting with a vibrant red, or a sunflower bathed in golden sunlight—both showcase a high level of saturation, grabbing our attention and conveying a sense of life and vibrancy. The world’s landscapes are a tapestry of color, from the emerald green of lush forests to the deep azure of the sky. Each hue possesses a specific saturation level, contributing to the overall harmony and beauty of nature.
Artistic Expression: Saturation and its Influence on Art
Artists across history have employed saturation as a fundamental tool in their creative endeavors. From the brushstrokes of Van Gogh in his iconic “Starry Night” to the bold patterns of Kandinsky’s abstract art, saturation plays a critical role in conveying emotions, setting a specific mood, and adding depth to a composition. A high-saturation palette can evoke excitement and energy, while muted colors create a sense of serenity or melancholy. The skillful manipulation of saturation allows artists to communicate their artistic visions effectively.
The Impact of Saturation in Design: From Websites to Logos
In the realm of visual design, saturation plays a pivotal role in creating engaging and effective design solutions. Website designers use saturated colors to draw attention to key elements on a webpage, while logo designers carefully select hues and their saturation levels to convey specific brand messages. For instance, a logo for a technology company might feature highly saturated blues and greens to evoke innovation and dynamism, while a logo for a luxury brand might employ rich, muted tones to communicate elegance and sophistication.
Understanding How We Perceive Saturation: The Science Behind the Experience
The Human Eye and its Sensitivity to Saturation
The way we experience color—and specifically, saturation—is largely influenced by our visual system. The human eye contains specialized cells called cones, which are responsible for detecting color. Different types of cones are sensitive to various wavelengths of light, allowing us to perceive a wide range of colors. Our perception of saturation is related to how much of a particular wavelength is stimulating the cones in our eye. A highly saturated color stimulates specific cones more intensely, leading to a stronger perception of a particular hue.
Context and Perception: How the Environment Affects Color
The environment surrounding a color can also impact its perceived saturation. For example, a rich, saturated red may appear less intense when placed against a background of bright yellow. The contrast between colors influences how we perceive their saturation levels. Our visual system automatically adjusts to account for the surrounding environment, ensuring that we can accurately perceive color variations.
The Potential of Saturation: Unlocking Creative Possibilities
Color Theory’s Power: Saturation is a Fundamental Element
Saturation is more than just a technical term; it’s a fundamental building block in color theory. Understanding how to manipulate saturation allows for more nuanced and expressive color choices in diverse creative endeavors. Whether you’re pursuing a career in art, design, or photography or simply seeking to enhance your appreciation of the world around you, a deeper understanding of color and its saturation is a valuable asset.
The Evolution of Color Theory: Saturation’s Expanding Role
The study of color theory is constantly evolving, as new technologies and research emerge. In recent years, digital tools have made it easier to manipulate saturation, creating unique artistic effects. Furthermore, an in-depth understanding of saturation is increasingly crucial in fields like color psychology, which explores the emotional and psychological impact of colors on individuals and their behavior.
What Is The Saturation Of A Color
Conclusion: Exploring a World of Color with Saturation
By understanding saturation, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the nuances of color and its power to express emotions, ideas, and emotions. From nature’s vibrant hues to the artistic palettes of masters, saturation plays a vital role in shaping our visual experiences. Whether you’re a seasoned artist, an aspiring designer, or simply someone captivated by the beauty of the world, delve into the world of color and explore the endless possibilities offered by saturation. It is a journey that will enrich your understanding of the world, ignite your creativity, and elevate your appreciation for the visual symphony that surrounds us.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




