Imagine walking into a crowded, bustling marketplace. Amidst the sights, smells, and sounds of commerce, you notice a unique order to the chaos. Vendors arrange their wares in specific locations, customers navigate with ease, and authorities oversee the exchange. This seemingly spontaneous scene is not simply a collection of individuals; it’s a reflection of the invisible structures called institutions that shape our social interactions. From market stalls to political systems, institutions permeate every aspect of our lives, providing the framework for our behavior and shaping our collective destiny.

Image: www.slideserve.com
Sociology, the study of human societies, recognizes the profound influence of institutions on individual lives and social structures. Understanding the complex interplay between individuals and institutions is crucial for comprehending how our societies function, evolve, and respond to change. In this exploration of institutions and sociology, we delve into the definition, history, and significance of these powerful social constructs.
The Foundation of Society: Defining Institutions
Institutions are established patterns of behavior, social arrangements, and norms that ensure the continuity and stability of social life. These are not physical structures but rather organized systems that dictate how individuals interact, make decisions, and pursue their goals. Think of institutions as blueprints for social action, providing guidelines and expectations for how society should operate.
Institutions are often characterized by their permanence, stability, and resistance to change. They endure over time, adapting and evolving in response to shifting social conditions yet retaining their core functions. Examples of institutions abound: education, healthcare, religion, law, government, economics, marriage, and family. These structures influence our beliefs, values, behaviors, and identities, shaping the very fabric of our existence.
The Historical Roots of Institutional Analysis
The study of institutions has a rich history, interwoven with the development of sociological thought. Early pioneers like Émile Durkheim emphasized the importance of social solidarity and collective consciousness, highlighting the role of institutions in maintaining social order. Max Weber, another prominent sociologist, focused on the impact of rationalization and bureaucracy on modern societies, emphasizing how institutions increasingly shape human behavior through formal rules and regulations. Through the lens of functionalism, sociologists like Talcott Parsons explored how institutions contribute to the stability and functioning of society by fulfilling essential needs and regulating social interactions.
Throughout the 20th century, the field of institutional analysis expanded, encompassing a diverse range of theoretical perspectives. Conflict theorists examine how institutions can perpetuate inequalities and power structures, while feminist theorists analyze the influence of gender on social institutions. Additionally, post-modernists challenge the notion of universal institutions, emphasizing the diversity and fluidity of social structures in a globalized world.
The Significance of Institutions in Sociology
Institutions are essential to sociology because they provide the lens through which we understand human behavior and social phenomena. By analyzing the dynamics of institutions, sociologists gain valuable insights into the following:
- Social Order and Stability: Institutions provide a framework for social order, establishing rules and norms that guide individual behavior and maintain societal equilibrium.
- Social Control and Regulation: Institutions like law, religion, and education regulate human behavior, ensuring compliance with societal norms and values.
- Socialization and Identity Development: Institutions play a crucial role in socializing individuals, shaping their beliefs, values, and sense of self. Families, schools, and religious organizations are primary examples of institutions that influence identity development.
- Power and Inequality: Institutions can be used to perpetuate existing power structures and inequalities, favoring certain groups and disadvantaging others.
- Social Change and Transformation: Institutions can be both sources of resistance to and drivers of social change. They can serve as agents of continuity but also undergo transformations in response to shifting social conditions and movements.
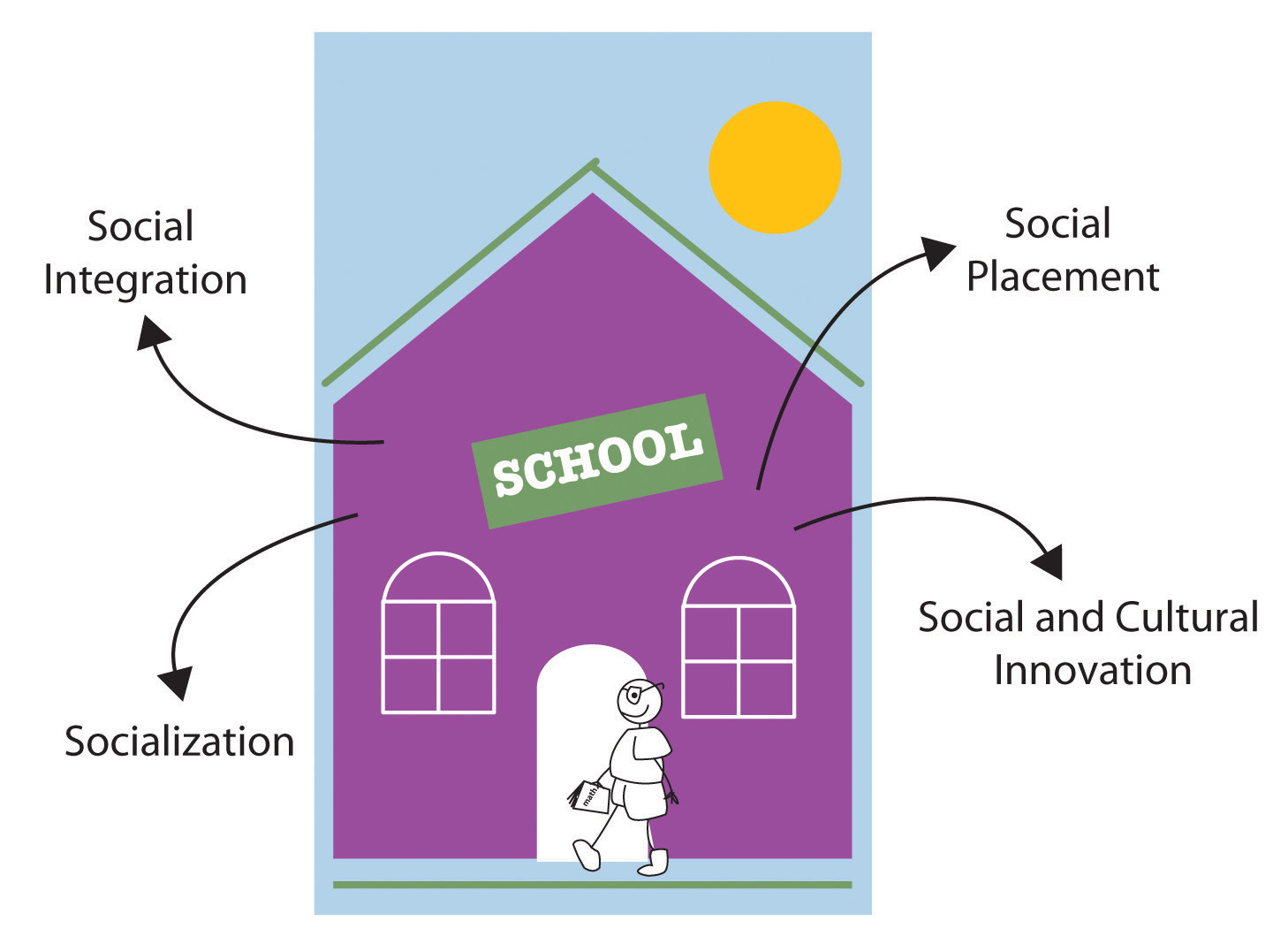
Image: pressbooks.howardcc.edu
Evolving Landscapes: Current Trends in Institutional Analysis
Institutions are not static entities; they constantly adapt and evolve in response to global transformations, societal pressures, and technological advancements. The 21st century has brought about a myriad of changes that are reshaping institutions across the globe. These emerging trends include:
- Globalization and Interconnectedness: Globalization has created interconnected networks and led to the diffusion of ideas, technologies, and institutions across national boundaries. This has resulted in a complex interplay of local and global institutions and their influence on societal dynamics.
- Technological Disruption: The rapid pace of technological advancements has ushered in new forms of communication, collaboration, and social interaction, significantly impacting institutions like education, work, and governance.
- Rise of Social Movements and Activism: Social movements, often fueled by social media and online platforms, are challenging existing institutions and demanding changes in areas such as gender equality, climate change, and social justice.
- Shifting Values and Norms: Societal values and norms are constantly evolving, leading to shifts in how institutions function and the expectations placed upon them. Issues like individual rights, diversity, and environmental sustainability are contributing to these changes.
- Increased Attention to Institutional Diversity: Social scientists are paying greater attention to the diversity of institutions across cultures and societies, recognizing that there is no single, universal model of social organization.
Expert Insights and Practical Tips
As a student of sociology, I’ve gained valuable insights into the intricacies of institutions and their impact on our lives. Here are some tips for navigating and understanding the ever-evolving landscape of institutions:
- Be an Active Citizen: Engage in local and global issues that affect your community and the world. Participate in discussions, advocate for change, and challenge unjust institutions.
- Embrace Critical Thinking: Question the assumptions and norms underpinning institutions. Analyze the power structures, biases, and inherent inequalities embedded within them.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Explore different perspectives on institutions from scholars, activists, and members of different communities. Recognize the multifaceted nature of social structures.
- Embrace Social Change: Understand that institutions are not static entities and can change in response to societal pressures. Be prepared to navigate and contribute to these shifts.
Remember, institutions are not simply abstract concepts but deeply intertwined with our daily lives. By understanding the complexities of these structures, we can better navigate social realities, participate in shaping our world, and work towards creating a more just and equitable society.
FAQ: Institutions and Sociology
Q: How do institutions influence individual behavior?
A: Institutions shape individual behavior through socialization, providing norms, values, and expectations. They influence how we think, act, and interact with others.
Q: Can institutions be changed?
A: Yes, institutions can change over time due to social movements, technological advancements, and shifts in societal values. However, change can be challenging because institutions often have a vested interest in maintaining the status quo.
Q: What is the role of institutions in promoting social justice?
A: Ideally, institutions should promote social justice by ensuring fairness, equality, and dignity for all individuals. However, institutions can also perpetuate inequalities if they are not critically examined and reformed.
Q: How does sociology contribute to our understanding of institutions?
A: Sociology provides a critical framework for analyzing the dynamics of institutions, their impact on society, and their potential for change. It allows us to see beyond the apparent structures and understand the underlying social forces at play.
Institutions Sociology
Conclusion
Institutions are the bedrock of society, shaping our interactions, our beliefs, and the course of our collective destiny. Sociology provides a valuable lens for understanding these powerful social structures, their influence on individual lives, and their potential for change. By engaging in critical analysis, seeking diverse perspectives, and actively participating in social discourse, we can navigate the evolving landscape of institutions and strive for a more equitable and just world. Are you interested in learning more about the intricate world of institutions?

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




