Imagine a young child, barely out of toddlerhood, watching their parents passionately discuss the latest political news. They may not understand the intricacies of the debate, but they absorb the energy, the emotions, and the beliefs expressed. This scene, commonplace in households across the globe, is a testament to the powerful process of political socialization. It’s the gradual and lifelong process through which individuals develop their political views, values, and beliefs. From the family dinner table to the classroom, from social media feeds to the news cycle, we are constantly bombarded with information and influences that shape our understanding of politics and our place in the political landscape.

Image: mddecoruae.com
This article delves into the fascinating world of political socialization, exploring its definition, key influences, and its impact on individuals and society. We will examine how our political views are shaped from a young age and how these views continue to evolve throughout our lives. We will also discuss the latest trends in political socialization and provide expert advice on navigating this complex process.
The Foundations of Political Socialization
Understanding the Process:
Political socialization is more than just absorbing political information. It involves a dynamic interplay between various agents of influence, social contexts, and the individual’s own interpretation and internalization of political ideas. It’s a process that begins early in life and continues throughout an individual’s lifespan, with each stage of development presenting new influences and opportunities for shaping political views.
Key Agents of Political Socialization:
Multiple agents contribute to political socialization, each playing a distinct role in shaping our political consciousness:
- Family: The family often acts as the primary agent of political socialization, transmitting values and beliefs that often shape a child’s initial understanding of politics. Children learn political attitudes and behaviors by observing their parents, siblings, and extended family members. The family’s political leanings, discussions about politics at home, and the way they engage with political issues heavily influence a child’s political development.
- School: Educational institutions also play a significant role in political socialization. Students learn about history, government, and current events, which contribute to their understanding of political structures, processes, and ideologies. The school environment can also foster critical thinking and civic engagement, encouraging students to participate in political discussions and debates.
- Peers: Peer groups exert a powerful social influence, shaping an individual’s identity and worldviews. As individuals interact with their peers, they are exposed to different perspectives on politics, potentially influencing their own opinions. The political culture within peer groups, ranging from casual conversations to organized political activism, can significantly impact a person’s political socialization.
- Media: The media, including television, newspapers, social media, and online platforms, serves as a powerful agent of socialization, providing information and shaping public opinion. The media’s coverage of political events, the perspectives presented, and the framing of issues greatly influence an individual’s understanding and perception of politics. However, the rise of “filter bubbles” and “echo chambers” on social media platforms has raised concerns about the potential for media to reinforce existing beliefs and limit exposure to diverse viewpoints.
- Religion: Religion can play a significant role in political socialization, shaping individual values and beliefs about social justice, morality, and the role of government. Religious institutions often hold specific political stances and advocate for particular policies, influencing their members’ political views. Religious leaders are also active in political discourse, often expressing their opinions and mobilizing congregations to support or oppose specific political initiatives.
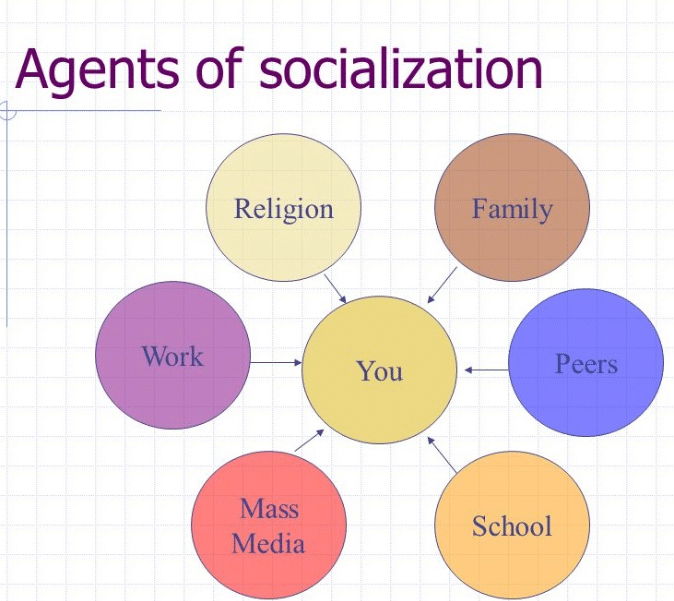
Image: educationisaround.com
The Dynamic Nature of Political Socialization
While many foundations of political socialization are laid during childhood and adolescence, the process continues throughout our lives. As individuals encounter new experiences, engage in critical thinking, and are exposed to diverse viewpoints, their political perspectives evolve and become more nuanced. Life events such as marriage, parenthood, or job changes can also significantly shape our political beliefs and priorities.
In a dynamic world, political socialization is not a one-way street. It’s a continuous interplay between internalization of existing values and beliefs and the individual’s own critical reflection and adaptation. Political socialization is a journey, not a destination. Our political views are not static and unchanging; rather, they are constantly evolving as we navigate the complexities of our political landscape.
Trends and Developments in Political Socialization
The digital age has dramatically transformed political socialization. Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have become powerful vehicles for political discourse and activism. While these platforms provide unprecedented access to information and opportunities for political engagement, they also pose challenges. The proliferation of misinformation, the spread of partisan propaganda, and the creation of echo chambers can polarize opinions and hinder constructive political dialogue.
Another significant development in political socialization is the growing importance of identity politics. Identity categories like race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, and religious affiliation increasingly influence political views and affiliations. This trend has led to a greater awareness of social inequalities and a more vocal advocacy for the rights and interests of marginalized groups. The rise of identity politics has also contributed to a more fragmented political landscape, with individuals aligning themselves with groups that share their identity experiences and concerns.
Tips and Expert Advice for Navigating Political Socialization
Here are some tips for navigating the complexities of political socialization:
- Be a Critical Consumer of Information: In the age of information overload, it’s essential to develop critical thinking skills. Be aware of potential biases in news sources and social media content, and actively seek out diverse perspectives. Don’t accept information at face value – question assumptions, look for evidence, and critically evaluate arguments.
- Engage in Constructive Dialogue: Rather than retreating into echo chambers, engage in respectful dialogue with people who hold different political views. Listen actively, be open to new perspectives, and seek common ground. Remember that meaningful political discourse often involves understanding and appreciating the viewpoints of those with whom you disagree.
- Be Informed and Engaged in Your Community: Participate in local political events, volunteer for causes you care about, and stay informed about issues that affect your community. By actively engaging in your community, you can contribute to shaping political discourse and influencing policy decisions.
Navigating the complex world of political socialization requires a commitment to lifelong learning, critical thinking, and engaging in civil discourse. Remember, political socialization is a journey, and your views will continue to evolve and adapt as you encounter new experiences and perspectives.
FAQ
Q: Is political socialization a lifelong process?
A: Yes, political socialization is a continuous process that begins in childhood and continues throughout life. Our political views are shaped by new experiences, social interactions, and evolving worldviews.
Q: What are some of the key influences on political socialization?
A: Family, school, peers, media, and religion are key agents of political socialization. Each plays a distinct role in shaping an individual’s political beliefs and attitudes.
Q: How can I become a more informed and engaged citizen?
A: Be a critical consumer of information, engage in constructive dialogue with people who hold different political views, and actively participate in your community. Stay informed about issues that affect you and consider volunteering for causes you care about.
Definition Political Socialization
Conclusion
Political socialization is a fundamental aspect of our societal and political landscape. We are all shaped by the influences of our environment, our experiences, and our interactions with others. By understanding the process of political socialization and its diverse agents, we can become more informed and engaged citizens, fostering meaningful dialogue while navigating the complexities of our political world.
Are you interested in learning more about the fascinating world of political socialization? Tell us about your experiences and perspectives in the comments below. We welcome your insights!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




