Imagine a bustling city park, filled with laughter, music, and the vibrant energy of families enjoying their day. You might think of this as a place for recreation and community building. But what about the unintended consequences? The park might also serve as a space for homeless individuals to find shelter or for street vendors to earn a living. These seemingly unplanned outcomes highlight the complex relationship between intended and unintended social effects, a fundamental concept explored in sociology through the lens of manifest functions and latent functions.
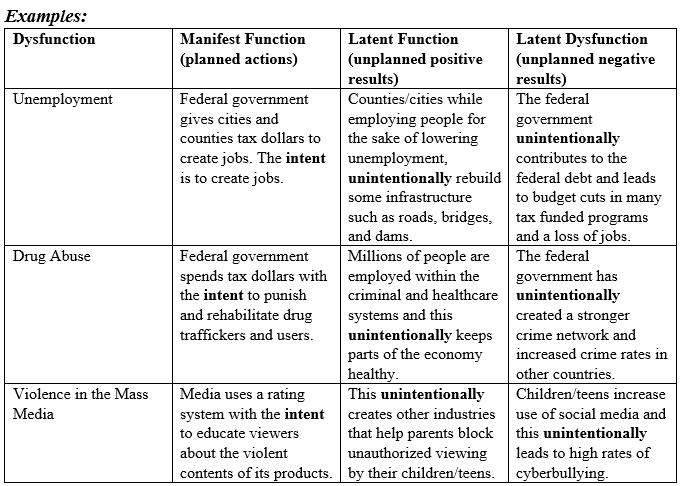
Image: www.mypromosource.com.au
This article delves into the world of manifest functions in sociology, exploring their definition, historical context, and real-world applications. We’ll unravel the intricate dynamics of intended social consequences, understanding how they shape our world and contribute to the complex tapestry of human interaction.
Defining Manifest Functions
In essence, a manifest function is the intended and recognized consequence of a social process or institution. It’s the primary reason why something exists, the explicit purpose that guides its creation and operation. Imagine a school, its manifest function is to educate students and prepare them for future careers and societal roles. This goal is clearly outlined in its curriculum, teaching methods, and organizational structure.
The concept of manifest functions was introduced by the American sociologist Robert K. Merton, who built upon Émile Durkheim’s earlier work on social facts. Merton recognized that social phenomena, whether institutions, practices, or even individual behaviors, have both intended and unintended consequences. The manifest function is the intended consequence, the one that society consciously seeks to achieve.
Exploring the Historical Context of Manifest Functions
The Evolution of Social Thought
The concept of manifest functions has its roots in the development of sociological thought. Early sociologists, such as Auguste Comte and Herbert Spencer, focused on understanding the social order and its evolution. However, it was Émile Durkheim who first formally introduced the concept of “social facts,” stressing that society operates according to its own laws and forces.

Image: www.youtube.com
The Legacy of Merton
Building upon Durkheim’s framework, Robert K. Merton made significant contributions to understanding social functions. His work emphasized the distinction between intended and unintended consequences, leading to the development of the “manifest function” and “latent function” concepts. Merton argued that social phenomena can have multiple functions, some intended and others, often overlooked, unintended.
Unveiling the Significance of Manifest Functions
Understanding manifest functions is crucial for comprehending how societies operate and how social change occurs. By examining the intended consequences of social institutions and practices, we can gain valuable insights into the values and priorities of a society.
Social Order and Stability
Manifest functions play a vital role in maintaining social order and stability. For example, the manifest function of the legal system is to enforce laws, deter crime, and uphold justice. This function, when effectively implemented, contributes to a sense of safety and security within society.
Social Values and Norms
Manifest functions often reflect the dominant values and norms of a society. Consider the manifest function of education, which aims to impart knowledge, critical thinking skills, and social values. These values are often embedded in the curriculum, classroom practices, and school policies, shaping young minds and contributing to the perpetuation of cultural values.
Modern Applications of Manifest Functions in Sociology
The concept of manifest functions remains a powerful tool for analyzing the complexities of the modern world. Sociologists utilize this framework to study various social phenomena, including:
Social Movements
Manifest functions can help us understand the motivations and goals of social movements. For example, the civil rights movement’s manifest function was to achieve racial equality and dismantle discriminatory practices.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements often have both intended and unintended consequences. The manifest function of the internet, for example, was to facilitate communication and information sharing. However, it has also led to unintended consequences such as online privacy concerns, social isolation, and the spread of misinformation.
Globalization
Globalization, with its interconnectedness and cultural exchange, presents opportunities and challenges. The manifest function of globalization is to promote economic growth and cultural exchange. However, its unintended consequences can include economic disparities, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization.
Tips and Expert Advice for Understanding Manifest Functions
To delve deeper into the concept of manifest functions, consider these tips and expert advice:
1. Look Beyond the Obvious
While the manifest function might seem readily apparent, it’s essential to critically examine the intended consequences and consider their implications for various stakeholders.
2. Consider Unintended Consequences
Don’t overlook the potential for latent functions, the unintended consequences that can emerge from social processes. These can be just as important as the manifest functions in shaping societal outcomes.
3. Analyze Different Perspectives
Recognize that different social groups and individuals may hold varying perspectives on the intended consequences of social phenomena. This can lead to competing interpretations of manifest functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is the difference between manifest functions and latent functions?
A: Manifest functions are the intended and recognized consequences of a social process, while latent functions are the unintended and often less obvious consequences.
- Q: Can a social process have both manifest and latent functions?
A: Absolutely! Many social processes have both intended and unintended consequences. For example, schools aim to educate students (manifest function) but may also contribute to social stratification (latent function).
- Q: How can identifying manifest functions be helpful for social change?
A: By understanding the intended goals of social institutions and practices, we can pinpoint areas for reform and work towards achieving more equitable and just outcomes.
- Q: Are manifest functions always positive for society?
A: Not necessarily. Manifest functions can sometimes have negative consequences or reinforce existing inequalities. For example, the manifest function of prisons may be to punish criminals, but they can also contribute to social marginalization.
- Q: How do manifest functions relate to social conflict?
A: Manifest functions can become points of contention when different social groups have conflicting values or priorities regarding intended outcomes. This can lead to social movements, protests, or even broader conflicts.
What Is A Manifest Function In Sociology
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LcluY6UsVXY
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of manifest functions in sociology is crucial for gaining a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay of intended and unintended consequences in shaping social life. The manifest function highlights the deliberate goals of social institutions and practices, shedding light on the values and priorities that guide a society’s evolution. As we continue to navigate the ever-changing landscape of the modern world, appreciating the interconnectedness of social forces and their intended outcomes will become increasingly important.
Are you interested in exploring the role of manifest functions in specific social issues or contexts? Share your thoughts!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




