Have you ever stopped to consider the global reach of the products you use daily? From the smartphone in your hand to the clothes on your back, chances are you’re interacting with goods and services produced by companies that operate across international borders. These entities, known as transnational corporations (TNCs), play a significant role in shaping the global economy, and their impact is felt in various aspects of our lives, from employment and technology to environmental sustainability and social justice.
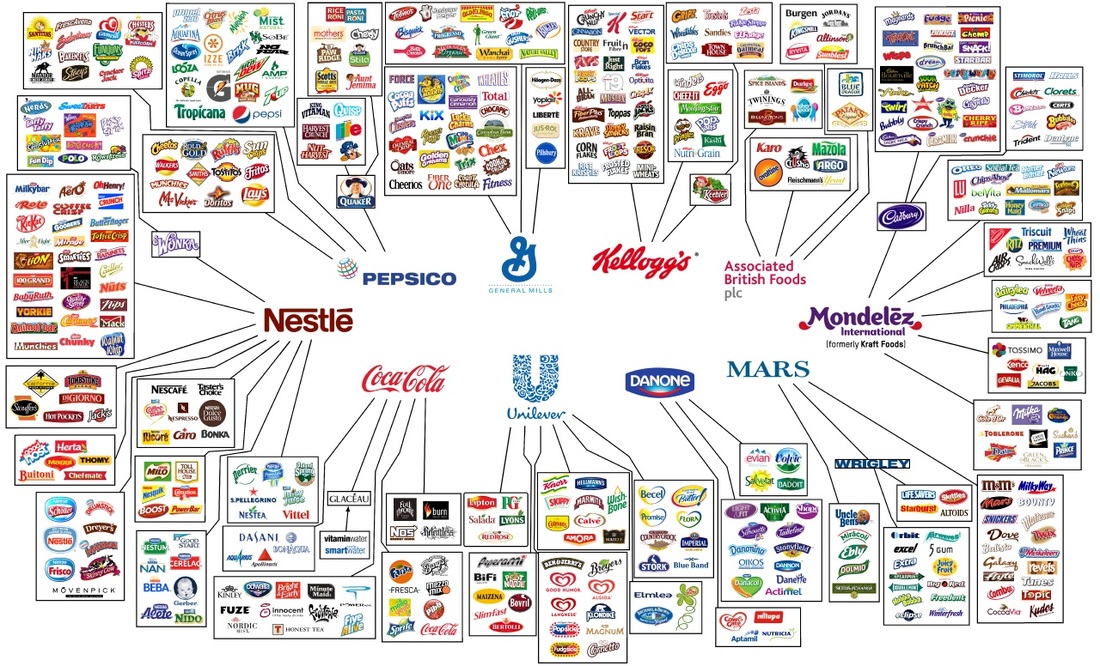
Image: bigfatrevision.blogspot.com
Understanding the nature and influence of TNCs is crucial in navigating the complexities of the modern world. This article explores the concept of TNCs, dives into notable examples, and examines their multifaceted impact on our society. We’ll delve into their history, analyze their diverse strategies, and explore the challenges and opportunities they present for both global development and individual well-being.
What are TNCs?
TNCs, often referred to as multinational corporations, are enterprises that operate in multiple countries beyond their country of origin. While the term “multinational” might be more familiar, “transnational” is generally preferred because it highlights the interconnectedness and global scope of their activities. These companies often have complex organizational structures, operate in diverse industries, and employ a vast workforce scattered across the globe.
Key Characteristics of TNCs
TNCs share several key characteristics:
- Global Reach: They operate in numerous countries, expanding their market share and maximizing their profits.
- Complex Organization: They often have headquarters in one country and subsidiaries or branches in others, fostering a network of operations.
- Diversified Activities: They engage in a range of activities, including manufacturing, marketing, research and development, and finance.
- Significant Influence: TNCs hold substantial economic power, impacting both national and international economies.
The Rise of TNCs: A Historical Perspective
The roots of TNCs can be traced back to the early days of colonialism, where European trading companies established networks across the globe. Industrialization in the 19th century further fueled the growth of multinational enterprises, driven by the need for raw materials and new markets. The post-World War II era witnessed a surge in the formation of TNCs, propelled by technological advancements, liberalization of trade policies, and globalization.

Image: www.diffzy.com
TNC Examples: Global Powerhouses
The world is teeming with TNCs, each leaving its unique mark on the global landscape. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Apple
Apple stands as a modern-day behemoth in the tech industry. With global headquarters in Cupertino, California, Apple designs, develops, and markets consumer electronics, software, and online services. Its iconic products, including iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers, have revolutionized the way people interact with technology. Apple’s global reach is evident in its vast network of retail stores, manufacturing partnerships, and online presence, making it a true transnational powerhouse.
2. Walmart
Walmart, based in Bentonville, Arkansas, is the world’s largest retailer by revenue. It operates a network of over 10,500 stores in 24 countries, offering a wide range of products at competitive prices. As a TNC, Walmart has faced criticism for its labor practices, environmental impact, and influence on local economies. However, its global presence and impact on consumer shopping habits are undeniable.
3. Toyota
Toyota, a Japanese automaker headquartered in Toyota, Aichi, has risen to become a global leader in the automotive industry. It manufactures and sells vehicles, engines, and other parts in numerous countries, including major manufacturing hubs in Japan, North America, and Europe. Toyota’s commitment to quality, efficiency, and innovation has made it a respected brand worldwide.
4. Nestle
Nestle, headquartered in Vevey, Switzerland, is a multinational food and beverage conglomerate. It is known for its wide portfolio of brands, including Nescafe, Kit Kat, Maggi, and Perrier. Nestle’s global reach extends to over 189 countries, making it one of the largest food companies in the world. It faces scrutiny over its sourcing practices, sustainability efforts, and marketing to children.
5. Microsoft
Microsoft, based in Redmond, Washington, is a tech giant renowned for its software and cloud computing services. Its operating systems, productivity software, and gaming platforms have become ubiquitous worldwide. Microsoft’s global presence is evident in its extensive network of offices, data centers, and research facilities, solidifying its position as a leading TNC.
The Impact of TNCs: Benefits and Challenges
TNCs exert a significant influence on global development and create both opportunities and challenges. They contribute to economic growth, technological advancement, and job creation. Their global operations connect people and markets, fostering international trade and the exchange of ideas. However, they also face criticism for their potential to exploit workers, weaken national sovereignty, and exacerbate environmental issues.
Positives:
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: TNC investments stimulate economic growth in host countries, creating jobs and generating tax revenue. Their large-scale operations provide employment opportunities, particularly in developing nations.
- Technological Advancement: TNCs often invest heavily in research and development, driving technological innovation and innovation with a global impact. They can also transfer technology and expertise to developing countries.
- Global Integration: TNCs contribute to global integration by fostering cross-border trade, investment, and cultural exchange. They connect markets and promote the flow of goods, services, and capital.
Negatives:
- Exploitation of Workers: TNCs have been accused of exploiting workers in developing countries, offering low wages, poor working conditions, and limited benefits. Labor rights issues and concerns over worker safety are often raised.
- Environmental Impact: TNC operations can contribute to environmental degradation, including pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion. Their global supply chains can lead to increased carbon emissions and biodiversity loss.
- National Sovereignty and Tax Avoidance: TNCs can influence national policies and regulations through lobbying efforts and tax avoidance strategies. Their power can challenge the sovereignty of nations and reduce government revenue.
The Future of TNCs: Challenges and Opportunities
As the global landscape continues to evolve, TNCs face a new set of challenges and opportunities. The rise of technology, increasing consumer awareness, and growing pressure for social and environmental responsibility are transforming the playing field.
Challenges:
- Increased Scrutiny and Accountability: TNCs are facing growing scrutiny from governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and consumers. Increased transparency and accountability are becoming crucial for maintaining their reputation and legitimacy.
- Evolving Global Landscape: New trade agreements, technological disruptions, and geopolitical shifts are creating uncertainty for TNCs. They need to adapt their strategies to navigate these complex challenges.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Consumers and investors are increasingly demanding sustainable and socially responsible practices from TNCs. Companies that fail to meet these expectations face reputational risks and investor backlash.
Opportunities:
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: TNCs have the capacity to drive innovation and harness new technologies to address global challenges. They can play a key role in developing solutions for climate change, poverty, and healthcare.
- Emerging Markets: TNCs can leverage their resources and expertise to enter and expand into emerging markets, contributing to economic development in regions with high growth potential.
- Building Partnerships: TNCs can forge partnerships with governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders to address complex social and environmental issues. Collaborative efforts can unlock new opportunities for sustainable development.
Tnc Examples
Conclusion
TNCs are integral players in the global economy, shaping the world we live in. They offer both benefits and challenges, and understanding their impact is crucial for informed decision-making. As TNCs continue to navigate the complexities of the modern world, they must embrace responsible practices, prioritize sustainability, and work collaboratively to address global challenges. Exploring the examples discussed in this article provides valuable insights into the nature, influence, and future of these powerful entities. By engaging with the topic of TNCs, fostering critical thinking, and advocating for ethical and sustainable practices, we can collectively harness their power for positive global change.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




