Have you ever stopped to ponder why your favorite band has millions of fans, or why certain clothing styles become wildly popular? Have you ever wondered about the complex dynamics of your own family or the social structures that shape your community? If so, you’re already exercising a sociological eye. This is the ability to look beyond the surface of everyday events and examine the underlying social forces that shape our lives.

Image: proessays.net
Sociology is the study of society, its structures, and its dynamics. It delves into the intricate web of human interactions, social groups, institutions, and cultural norms that define our experience. By understanding the principles of sociology, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human behavior and the interwoven relationships that bind us together. This knowledge can empower us to navigate social landscapes with greater awareness, engage with diverse perspectives, and contribute to building a more just and equitable society.
The History of the Sociological Eye
The idea of looking at society with a critical lens dates back centuries, but sociology as a formal discipline emerged in the 19th century, driven by profound social and economic changes. The Industrial Revolution brought about rapid urbanization, social upheaval, and new forms of social organization, prompting thinkers like Auguste Comte, Karl Marx, and Emile Durkheim to seek scientific explanations for these transformations. These early sociologists recognized the need to break down complex social phenomena into manageable units of analysis, applying rigorous methods of observation, data collection, and interpretation to understand the forces at play.
Core Concepts: Building Blocks of Social Understanding
To understand the world through a sociological eye, it’s essential to grasp some fundamental concepts that form the basis of sociological analysis:
Social Structure
Societies are organized into interconnected structures, like families, schools, workplaces, and governments. These structures define our roles, expectations, and relationships, shaping how we interact and behave.
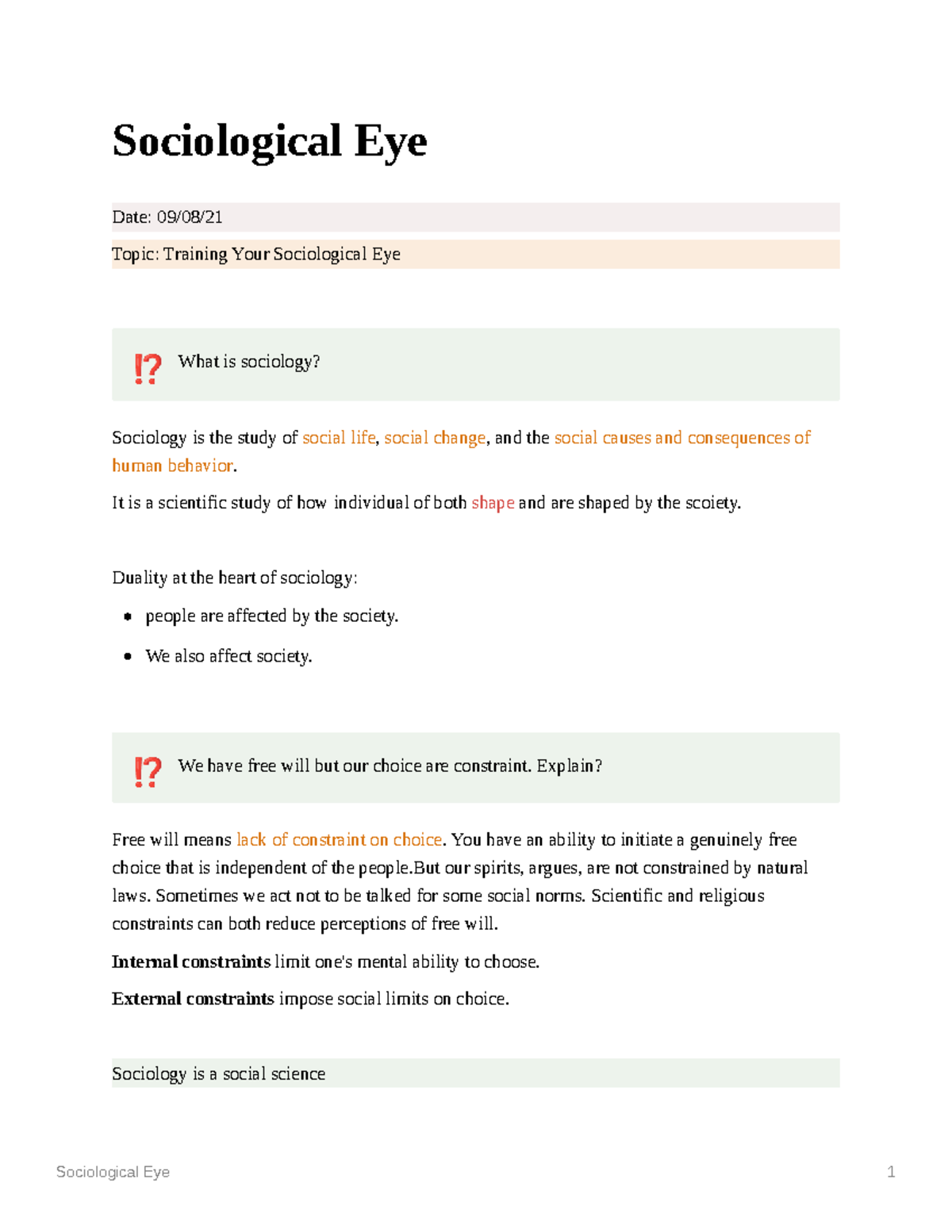
Image: www.studocu.com
Social Norms
These are the unwritten rules and expectations that guide behavior within a society. Norms can range from subtle social cues to explicit laws, and they are vital for maintaining order and social stability.
Culture
Culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, practices, and material objects of a group of people. Culture provides a framework for understanding the world, interpreting experiences, and guiding behavior.
Socialization
This is the process through which individuals learn the social norms, values, and beliefs of their culture, becoming members of society. Socialization begins from birth and continues throughout life, shaping our identities and influencing our behaviors.
Social Inequality
This refers to the uneven distribution of resources, power, and opportunities within a society. Social inequality can be based on factors like race, gender, class, and sexual orientation, leading to disparities in access to education, healthcare, and economic advancement.
The Sociological Eye: Unraveling Everyday Phenomena
By applying these core concepts, we can begin to see everyday phenomena in a new light. For instance, consider a simple act like choosing a restaurant for dinner.
The Sociology of Dining
On the surface, it might seem like a personal decision based on taste preferences. But a sociological eye reveals a broader range of factors at play:
- Social class: Your choice of restaurant might be influenced by your economic status, with different income levels affording access to various dining options.
- Cultural tastes: Your preferences might reflect your cultural background, with specific cuisines associated with particular ethnic groups or regions.
- Social norms: Choosing a restaurant that aligns with your social group’s norms increases conformity and reinforces group identity.
- Social capital: Dining out can provide opportunities for social networking and building relationships, especially in professional or business settings.
Beyond Dining: Applying the Sociological Eye
This same approach can be applied to countless other aspects of life, from fashion and music choices to political activism and social movements. By asking “why?” and examining the underlying social dynamics, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces shaping our world.
The Impact of the Sociological Eye
The sociological perspective can empower individuals and communities in a variety of ways:
- Enhanced empathy and understanding: Understanding the social forces that shape individual behavior can promote empathy and tolerance for different perspectives.
- Informed decision-making: By analyzing social patterns, we can make more informed decisions about personal choices, political activism, and social policy.
- Social change and progress: Sociology provides tools for promoting social justice and addressing issues like poverty, inequality, and discrimination.
- Building stronger communities: By understanding the dynamics of social groups, we can create more inclusive and supportive communities.
The Future of Sociology: Emerging Trends and Discoveries
Sociology is an ever-evolving field, continually adapting to new social challenges and technological advancements. Here are some emerging trends shaping the future of the discipline:
- The digital age: The rise of social media and online platforms has created new forms of social interaction, collective behavior, and social movements. Sociologists are exploring the ways these technologies are redefining our relationships, shaping public opinion, and influencing political outcomes.
- Globalization and interconnectedness: As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, sociologists are examining the impact of globalization on social structures, cultures, and inequalities.
- Climate change and sustainability: The growing threat of climate change has prompted new research on environmental justice, sustainable development, and the social dimensions of climate action.
- Social psychology and neuroscience: The integration of insights from social psychology and neuroscience is providing a deeper understanding of the biological and psychological underpinnings of social behavior.
Sociological Eye
Conclusion: The Importance of Seeing the World Through a Sociological Eye
By learning to see the world through a sociological eye, we can deepen our understanding of ourselves, our communities, and the world around us. By embracing the principles of sociological analysis, we can critically examine social dynamics, challenge preconceived notions, and contribute to building a more equitable and just society. As we navigate complex social landscapes, the sociological perspective provides a powerful tool for navigating challenges, fostering meaningful dialogue, and shaping a more positive future for all.
Further Exploration:
- Explore the works of renowned sociologists: Read books or articles by scholars like C. Wright Mills, Erving Goffman, and Michel Foucault.
- Join a sociological organization: Connect with like-minded individuals and engage in dialogue about current social issues.
- Take a sociology class: Gain a deeper understanding of sociological concepts and methodologies by taking a course at your local college or university.
The sociological eye is not just for academics; it’s a valuable tool for anyone who wants to understand the world around them and make a difference. So, look around you, observe, question, and engage with the social fabric of your life. You’ll be amazed at what you discover.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




