Have you ever wondered what whispers beneath the rhythmic thump of your heart? The silent symphony playing in your chest is a complex dance of electrical signals, a language that cardiologists decipher to understand your heart’s health. Within this intricate communication, there’s a tiny wave called the “P wave,” and when it flips, it can send a shiver down the spine of any medical professional. This article delves into the enigma of inverted P waves, exploring their significance, potential causes, and what they might mean for your well-being.
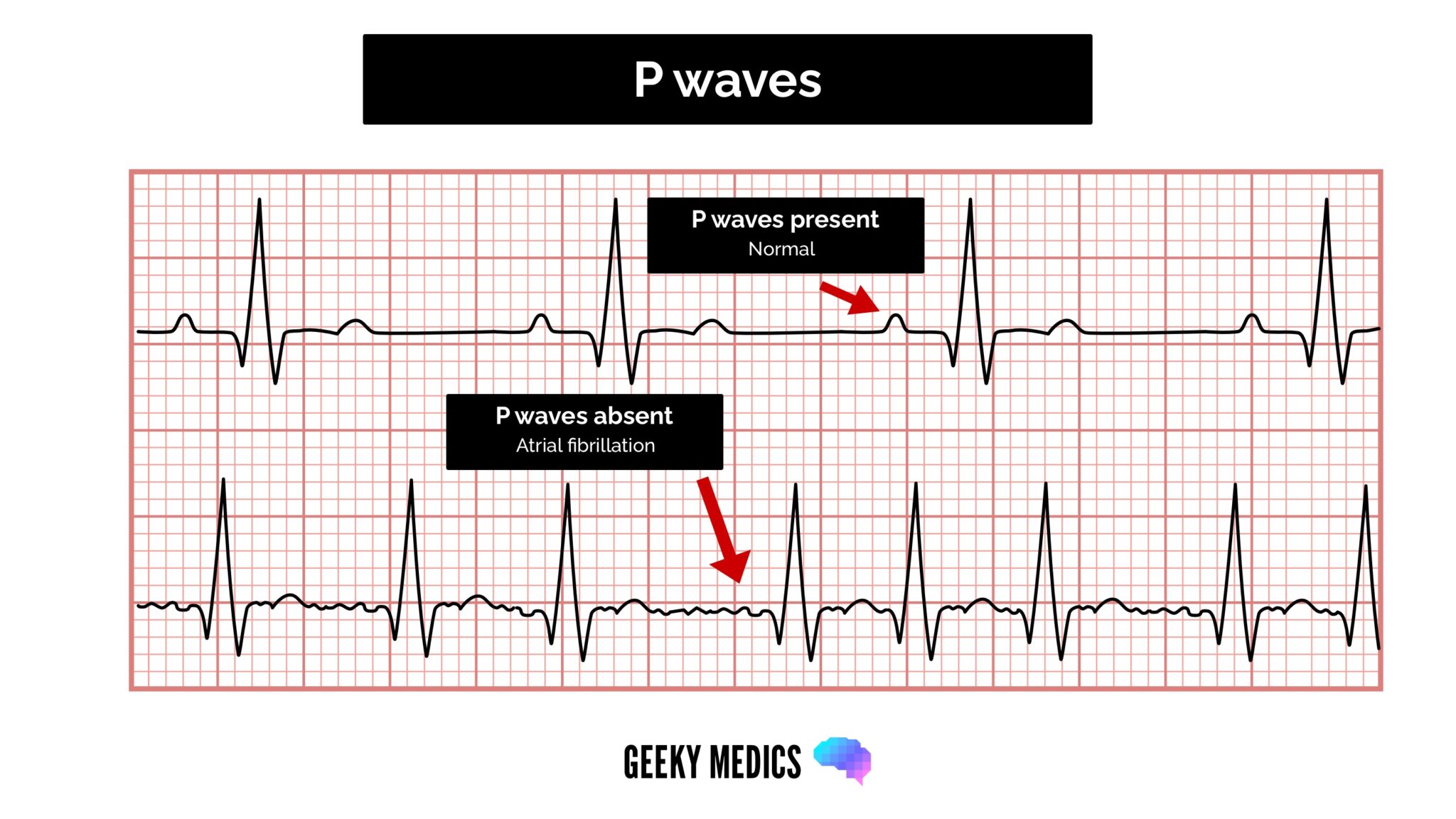
Image:
While you may not feel them directly, these tiny electrical signals are vital for keeping your heart beating, pumping life-sustaining blood through your body. An inverted P wave signifies a change in the usual rhythm of your heart, a flicker in the symphony that could point to an underlying condition deserving attention. So, let’s unravel the mystery of these inverted P waves together – understanding what they mean and how to navigate them with expert guidance.
Delving into the World of Inverted P Waves
To grasp the significance of an inverted P wave, we must first understand the intricate mechanics of the heart’s electrical system. The heart, a remarkable organ, beats thanks to a synchronized electrical current traveling through its chambers. This current is initiated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s natural pacemaker, and it triggers a series of electrical impulses that travel through the heart, causing it to contract and pump blood.
The P wave, a small bump on an electrocardiogram (ECG), represents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the atria, the heart’s upper chambers. It’s a crucial marker of the heart’s function, and its normal pattern is a small, upward deflection. However, when this wave flips and appears as an inverted or negative deflection, it can indicate a change in the electrical pathway as the signal travels through the atria.
Why Inverted P Waves Matter: A Deeper Dive
The presence of an inverted P wave is not inherently a cause for concern. It can be a harmless variant, a quirk of individual anatomy, or a sign of a temporary issue. However, in some cases, it can be a clue to more serious underlying conditions that warrant further investigation.
Several factors can contribute to inverted P waves, including:
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD): This birth defect occurs when there is a hole in the wall that separates the heart’s upper chambers, the atria. This hole can interfere with the normal flow of blood and disrupt the electrical signals, causing inverted P waves.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: This congenital condition involves an extra electrical pathway in the heart that can lead to rapid heartbeats and, in some cases, inverted P waves.
- Left Atrial Enlargement: An enlarged left atrium can distort the electrical signals, resulting in inverted P waves.
- Right Ventricular hypertrophy: Over time, the right ventricle can thicken if it has to work harder to pump blood through the lungs. This thickening can affect the electrical signals and lead to inverted P waves.
Decoding the ECG: What the Wave Tells Us
The ECG, like a silent storyteller, reveals valuable insights into the heart’s electrical activity. When a cardiologist interprets an ECG, they look for a variety of aspects, but the P wave holds a special significance.
- Amplitude: The height of the P wave can reveal the strength of the atria’s contraction, while its width gives an idea of the time it takes for the electrical signal to travel through the atria.
- Orientation: The P wave’s direction, whether it’s upright or inverted, reveals the electrical current’s path through the heart. An inverted P wave signals a change in this path, potentially due to anatomical variations or an underlying health issue.
- Shape: Even the shape of the P wave can be informative. A broadened or notched P wave might suggest an enlarged atrium or slowed electrical conduction through the heart.

Image: jhcedecg.blogspot.com
Interpreting Inverted P Waves: A Journey Through the Heart’s Language
Not all inverted P waves are cause for alarm. Many factors can contribute to their appearance, including:
- Lead Placement: The electrode placement on the patient’s chest during an ECG can influence the wave’s appearance.
- Rhythm Variations: Some normal heart rhythms, like sinus bradycardia, can manifest as inverted P waves due to the slowing of the heart rate.
- Individual Variations: The heart’s electrical pathways can vary significantly between individuals leading to differences in ECG waveforms, including the P wave.
However, it’s important to be aware that inverted P waves can sometimes signal a serious underlying issue, such as:
- Atrial Fibrillation or Flutter: In these conditions, the heart’s upper chambers beat irregularly and chaotically, often leading to an irregular P wave pattern or even absence, including inverted P waves.
- Heart Block: This condition occurs when there is a delay or disruption in the electrical signals traveling through the heart. Different types of heart blocks can manifest as inverted P waves.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Elevated pressure in the arteries of the lungs can lead to right ventricular hypertrophy, which can also cause inverted P waves.
Navigating the Inverted P Wave: Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
If you discover an inverted P wave on your ECG, don’t panic. It’s critical to understand that an inverted P wave on its own isn’t necessarily a cause for worry. It could be merely a variation in the normal heart’s electrical rhythm or a sign of a temporary issue.
However, it’s essential to have it evaluated by a qualified medical professional, especially if it’s persistent or accompanied by other symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, or palpitations.
Expert Guidance for Taking Charge of Your Heart Health
Here are some tips from leading cardiologists to help you navigate the situation:
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your primary care physician to discuss your overall health and any concerns you have about your heart.
- ECG Evaluation: If you receive an ECG that reveals an inverted P wave, it’s crucial to discuss it with your doctor to understand its potential implications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help promote optimal heart health.
- Seeking Expert Opinion: If your inverted P wave is accompanied by other symptoms or your doctor recommends further evaluation, don’t hesitate to consult a cardiologist for a comprehensive assessment.
Inverted P Waves
Empowering Yourself Through Knowledge and Action
Understanding the intricacies of inverted P waves and their potential implications is a powerful step towards taking charge of your heart health. By embracing knowledge and actively communicating with your healthcare providers, you can navigate this diagnosis with confidence and make informed decisions about your well-being. Remember, early detection and proactive management play a vital role in safeguarding your cardiovascular health and ensuring a brighter future for your heart.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




