Have you ever wondered what eye color your children might inherit? It’s a question that has fascinated people for centuries, and while we can’t predict with certainty, understanding the genetics behind eye color can offer insights into the possibilities. The interplay of blue and brown eyes, two of the most common eye colors, creates a fascinating spectrum of possibilities for future generations.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Eye color is a complex trait, determined by multiple genes, with the most influential gene known as OCA2. This gene produces a protein called P protein, which plays a crucial role in melanin production. Melanin, a pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color, dictates the shade of your eyes. The more melanin present, the darker the eyes. Blue eyes result from a lack of melanin, while brown eyes contain higher amounts. Understanding how these genes interact allows us to explore potential eye color combinations for children.
The Basics of Eye Color Inheritance
The Power of Recessive and Dominant Genes
Eye color inheritance is a captivating example of Mendelian inheritance, where dominant and recessive genes influence the traits passed down. A simplified explanation often involves two primary genes: the brown eye gene (B), which is dominant, and the blue eye gene (b), which is recessive. If any version of the brown eye gene is present, it will overshadow the blue eye gene.
For instance, a person with a dominant brown eye gene (BB) will have brown eyes. Similarly, a person with one brown eye gene and one blue eye gene (Bb) will also have brown eyes. The only way to express the recessive blue eye color is to inherit two copies of the blue eye gene (bb).
Unraveling the Complexity of Eye Color Inheritance
While the brown and blue eye gene model provides a starting point, it’s merely the tip of the iceberg. Eye color inheritance is far more intricate than this simplistic explanation suggests. Numerous other genes influence eye color, adding layers of complexity and creating possibilities beyond simple brown and blue.
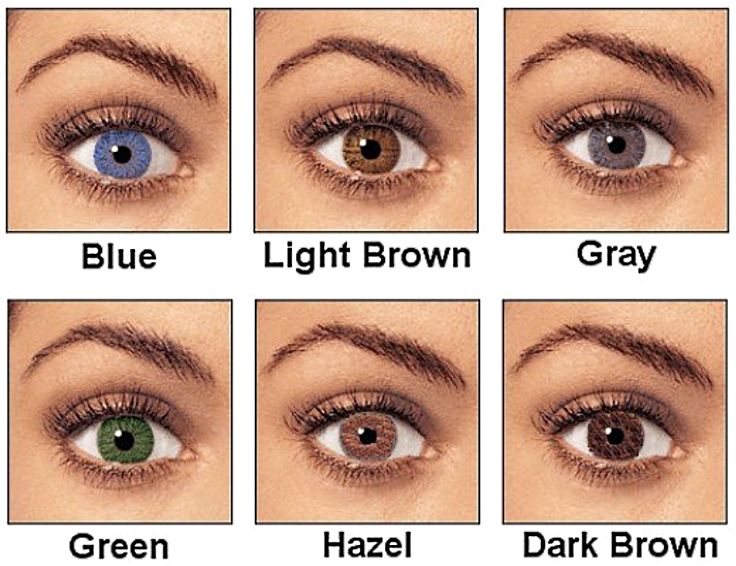
Image: www.qnaguides.com
The GEY gene: Another Key Player
The GEY (grey) gene plays a significant role, particularly in determining eye colors within the blue-brown spectrum. The GEY gene acts as a modifier, influencing how melanin is expressed in the iris. This gene can take multiple forms, impacting the shades of blue, green, and hazel eyes.
Beyond Two Genes
Beyond the OCA2 and GEY genes, numerous other genes contribute to eye color, creating an intricate tapestry of possibilities. For example, genes responsible for pigmentation in the skin and hair can impact eye color as well. The complexity of these genetic interactions makes predicting eye color in children a fascinating and challenging endeavor.
Exploring the Nuances of Blue and Brown Eye Combinations
Blue Eyes and Blue Eyes
A couple with blue eyes can only produce blue-eyed children. This happens because both parents contribute two recessive blue eye genes (bb). Their offspring inherit two copies of the blue eye gene, resulting in blue eyes.
Blue Eyes and Brown Eyes
A couple with one blue-eyed parent (bb) and one brown-eyed parent (BB or Bb) presents a more interesting scenario. The brown-eyed parent carries either two copies of the dominant brown eye gene (BB) or one brown and one blue eye gene (Bb).
If the brown-eyed parent is BB, their children will have brown eyes (Bb). If the brown-eyed parent is Bb, their children have a 50% chance of having brown eyes (Bb) and a 50% chance of having blue eyes (bb).
Brown Eyes and Brown Eyes
Two brown-eyed parents present the widest range of possibilities. They can each have two dominant brown eye genes (BB), one dominant and one recessive gene (Bb), or two recessive blue eye genes (bb).
Here’s how the combinations work out:
* **BB and BB** – All children inherit brown eyes (BB).
* **BB and Bb** – All children inherit brown eyes (BB or Bb).
* **BB and bb** – All children inherit brown eyes (Bb).
* **Bb and Bb** – 75% chance of brown eyes (BB or Bb) and 25% chance of blue eyes (bb).
* **Bb and bb** – 50% chance of brown eyes (Bb) and 50% chance of blue eyes (bb).
* **bb and bb** – All children inherit blue eyes (bb).
The Magic of Hazel Eyes
Hazel eyes, characterized by their captivating blend of brown, golden, and green hues, often result from the interplay of brown, blue, and green-related genes. The presence of blue and brown eye genes, along with modifiers like GEY, can lead to these mesmerizing eye colors.
The Role of Ancestry and Environment in Eye Color
While genetics plays the primary role in determining eye color, other factors contribute to the final hue. Ancestry and environment are believed to influence how genes are expressed.
Ancestry and Eye Color
Different ethnicities have varying frequencies of eye color genes. In populations of European descent, blue eyes are more prevalent, while in populations of African or Asian descent, brown eyes are more common. This pattern reflects the geographical distribution of eye color genes over many generations.
Environment and Eye Color
The environment can impact how genes are expressed, including light exposure. Sun exposure can slightly darken the iris, making brown eyes appear more intense. This influence is temporary, and the underlying genetic makeup remains unchanged.
The Fascinating Evolution of Eye Color
The evolution of eye color is a captivating story of genetic adaptation. Early humans likely had brown eyes, as melanin provides protection from harmful UV radiation. As humans migrated to regions with reduced sunlight, the need for high melanin levels decreased, leading to the development of blue eyes.
This adaptation allowed individuals living in northern latitudes to absorb more light, improving their vision in low-light conditions. It’s a remarkable example of how natural selection can shape human traits.
Eye Color: More Than Just Aesthetics
Eye color is not just a matter of appearance. It’s linked to various health conditions and traits. For example, people with lighter eye colors may be more susceptible to certain cancers, while people with darker eye colors may have a higher risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Research is ongoing to uncover the deeper connections between eye color and health. Understanding these relationships can lead to new strategies for disease prevention and treatment.
Blue And Brown Eyes Make What Color
Conclusion: The Enduring Mystery of Eye Color
Eye color is a captivating trait that continues to fascinate scientists and laypeople alike. While we’ve made significant strides in understanding the genetic mechanisms behind eye color, much remains to be discovered. The interplay of various genes, environment, and ancestry adds layers of complexity to this intriguing human characteristic.
Exploring the mystery of eye color is a rewarding journey into the world of human genetics. It reminds us that the seemingly simple traits we observe are often products of intricate genetic processes that have shaped our species over millions of years. So next time you gaze into someone’s eyes, remember the fascinating story they tell of genes, adaptation, and our shared human heritage.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




