Have you ever taken a stunning photograph, only to be disappointed by the dullness of its colors? Or perhaps you’ve had a vision for a vibrant, artistic piece that needs a color makeover? Photoshop, the industry standard for image editing, empowers you to transform any photo into a masterpiece through color manipulation. Whether you’re a beginner learning the ropes or a seasoned photographer seeking advanced techniques, discovering the secrets of color correction in Photoshop can unlock a world of creative possibilities.
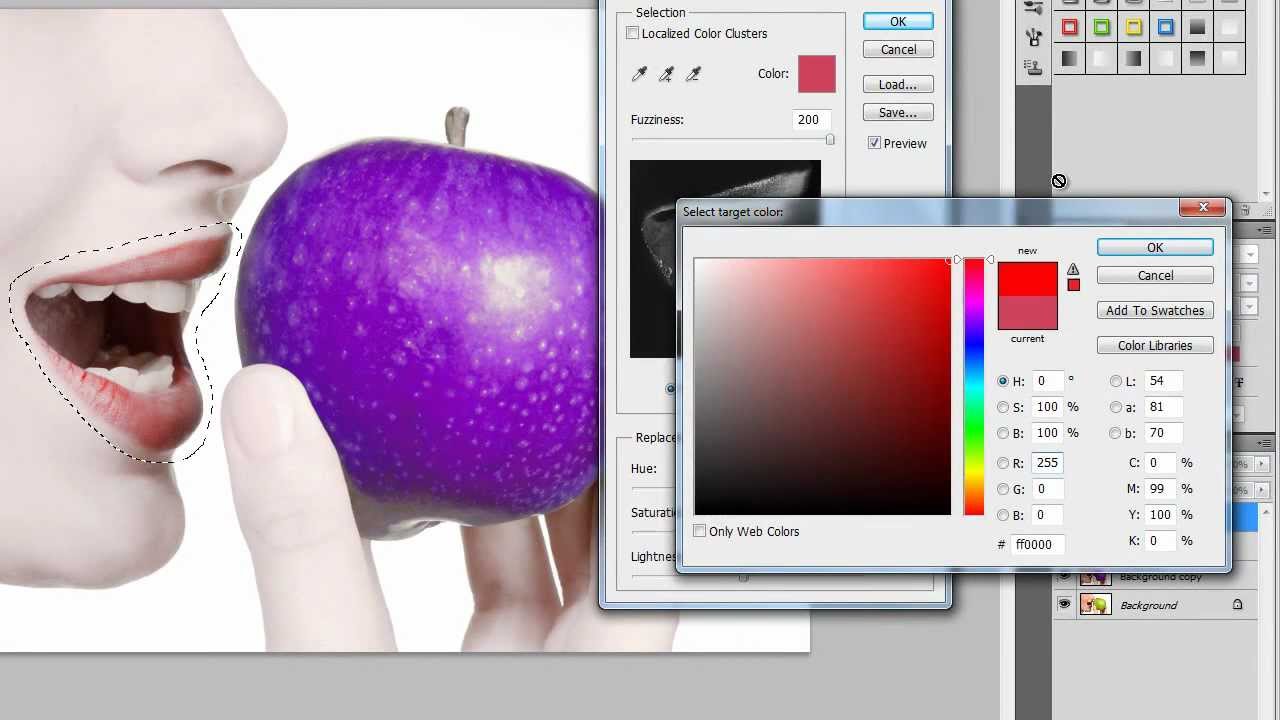
Image: sagazconcursos.blogspot.com
Imagine effortlessly turning a sunset sky from a washed-out orange to a mesmerizing fiery red, or giving a vintage image a modern, vibrant feel. This article will guide you through the essential tools and techniques to effortlessly change picture colors in Photoshop, empowering you to create impactful and visually arresting images.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Hue, Saturation, and Brightness
Before diving into the tools, let’s clarify the core concepts behind color manipulation: Hue, Saturation, and Brightness (HSB). Think of these as the building blocks of color:
- Hue: Refers to the pure color itself, like red, blue, or green.
- Saturation: Determines the intensity or purity of a color. A highly saturated color is bold and vivid, while a desaturated color is dull and muted.
- Brightness: Controls the lightness or darkness of a color. A bright color is closer to white, while a dark color is closer to black.
By mastering the interplay of HSB, you can fine-tune your image’s color to achieve the desired effect.
The Hue/Saturation Adjustment Layer: Your Color Alchemy Tool
The Hue/Saturation adjustment layer is a powerful non-destructive tool that offers precise control over color changes in Photoshop. Here’s how to use it:
- Open your image in Photoshop: Navigate to the “Layer” panel and click on the “Create new fill or adjustment layer” icon. Choose “Hue/Saturation” from the list of options.
- Adjust Hue, Saturation, and Lightness: The Hue/Saturation window will appear. Adjust the sliders for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness to manipulate the colors in your image.
- Hue: Rotate colors around the color wheel. For example, a positive Hue shift will move colors towards the red side of the spectrum, while a negative shift moves them towards the blue side.
- Saturation: Increase or decrease the color intensity. Moving the slider to the right increases saturation, making colors more vivid. Moving it to the left decreases saturation, making colors more muted.
- Lightness: Control the overall brightness of the image. Moving the slider to the right makes the image brighter, while moving it to the left darkens it.
- Target Specific Colors: The Hue/Saturation window also includes a color picker. Click the dropdown menu to select a specific color range and apply adjustments only to that range. This gives you precise control over altering specific elements of your image, like the sky or a subject’s clothing.
- Mastering Colorization: The Hue/Saturation window also allows you to colorize your image. Simply check the “Colorize” box, and adjust the Hue slider to choose your desired color. The Saturation slider will then control the intensity of the applied color.
The Hue/Saturation adjustment layer is your secret weapon for subtle color refinement or bold artistic transformations. Experiment with different settings and discover the magic you can create with this simple yet powerful tool.
Beyond Hue/Saturation: Other Color Adjustment Techniques
While the Hue/Saturation adjustment layer is a cornerstone, Photoshop offers a wealth of other tools to refine and transform colors in your image. Here are a few to explore:
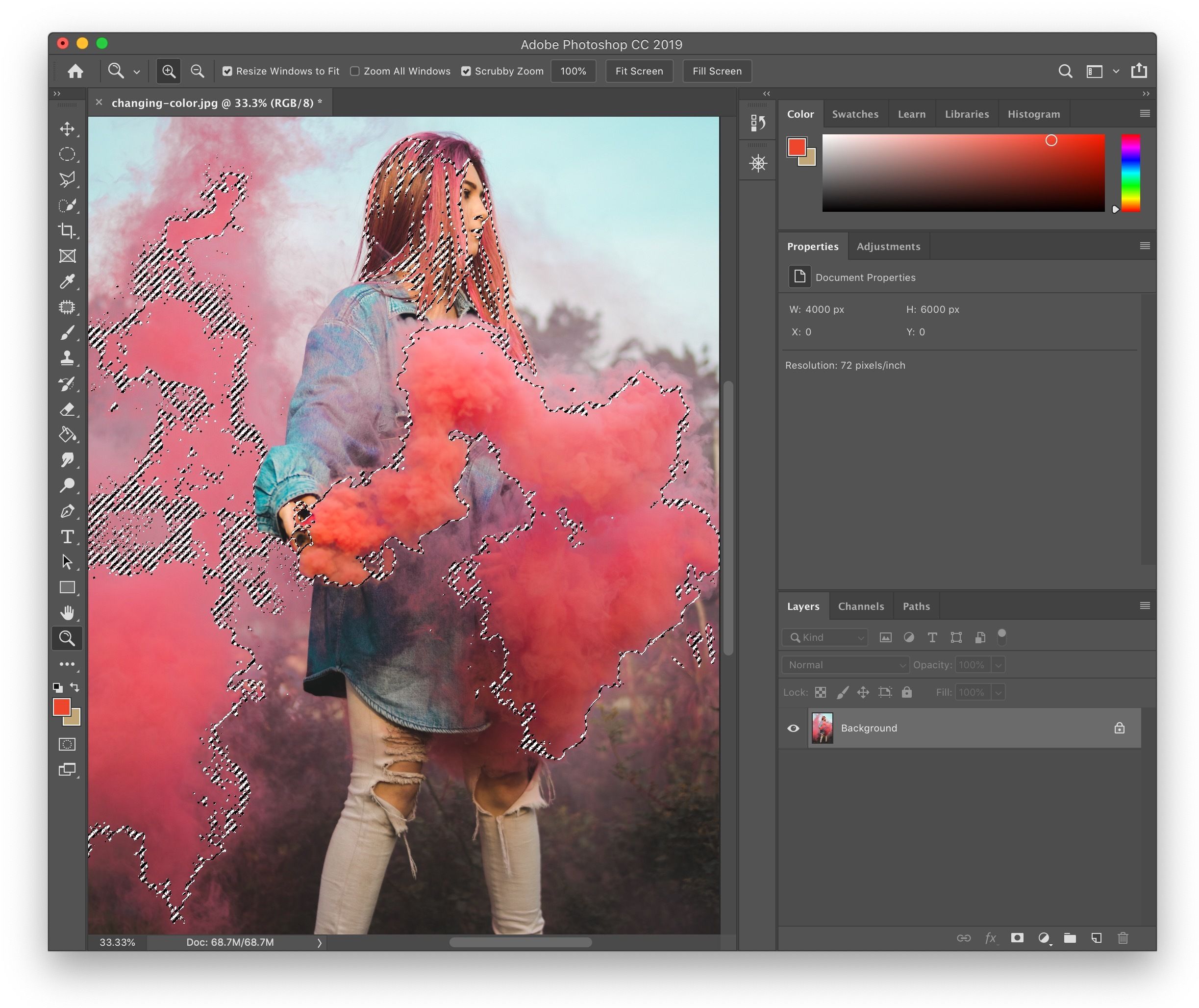
Image: giggster.com
1. The Levels Adjustment Layer
The Levels adjustment layer provides precise control over an image’s contrast and tonal range. It works by adjusting the distribution of light and dark pixels, which can effectively alter the perception of colors.
- Adjusting the Input Levels: The Levels window presents three sliders: Black, White, and Gray.
- The Black Point slider controls the darkest pixels in your image. Moving it to the right lightens the blacks.
- The White Point slider controls the brightest pixels. Moving it to the left darkens the whites.
- The Gray Point slider influences the midtones. You can use this to adjust the overall brightness of the image.
- The Histogram and Levels: The Levels window also features a histogram, a graphical representation of the distribution of light and dark values in your image. By observing the histogram, you can understand the image’s current tonal range and make informed adjustments to the Levels sliders to achieve a balanced and visually appealing result.
2. The Color Balance Adjustment Layer
The Color Balance adjustment layer offers control over the relative amounts of red, green, and blue in your image. This allows you to fine-tune the overall color temperature and create specific color casts.
- Adjusting the Color Balance: The Color Balance window presents sliders for shadows, midtones, and highlights. Dragging the sliders for red, green, or blue in the shadows, midtones, or highlights will shift the color balance of your image towards warmth or coolness. For example, adding more blue to the shadows can make them cooler, while adding more red to the highlights can make them warmer.
- Color Temperature: Color temperature, often measured in Kelvin, refers to the perceived warmth or coolness of a light source. A warm light source leans towards orange and yellow hues, while a cool light source leans towards blue and purple hues. The Color Balance tool allows you to fine-tune this aspect of your image.
- Creative Color Casts: The Color Balance tool is excellent for adding artistic color casts to your photos. You can create a vintage look by adding a warm yellow cast to the midtones or achieve a moody, dramatic feel by adding a cool blue cast to the shadows.
The Levels and Color Balance adjustment layers, along with the Hue/Saturation tool, provide a comprehensive toolkit for enhancing, refining, and manipulating the color palette of your images.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Color Manipulation
As you become more comfortable with Photoshop’s basic color adjustment tools, you can delve into advanced techniques to unlock even greater creative potential.
1. selective Color: Fine-Tuning individual Colors
The Selective Color adjustment layer provides an incredible level of control over individual colors in your image. It works by manipulating the relative amounts of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK) within a selected color range.
- Targeted Color Adjustment: Select a specific color range from the dropdown menu in the Selective Color window. For example, you can select “Reds” to specifically adjust the red hues in your image.
- CMYK Control: The Selective Color window presents sliders for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black.
- Cyan: Adding Cyan makes a color more bluish.
- Magenta: Adding Magenta makes a color more reddish.
- Yellow: Adding Yellow makes a color more yellowish.
- Black: Adding Black decreases the lightness of a color.
- Color Enhancement: The Selective Color tool can be used to enhance the vibrancy of existing colors or create unique color casts. For example, you can amplify the blues in a sky by adding a bit of Cyan or create a vintage look by adding a touch of Yellow to the reds.
2. Gradient Map: Creating Smooth Color Transitions
The Gradient Map adjustment layer allows you to apply a gradient to your image, creating a seamless transition between colors. This is a powerful tool for adding artistic flair and creating unique color palettes.
- Gradient Options: The Gradient Map window presents a variety of built-in gradients, or you can create your own custom gradients using the Gradient Editor. Choose a gradient that complements the theme and mood of your image. For example, a cool-to-warm gradient with blue hues transitioning to yellow hues can create a sunrise-like effect.
- Applying the Gradient: Applying the Gradient Map to your image will map the luminance values of your pixels to the gradient you selected, creating a smooth and artistic color transition.
- Artistic Possibilities: Gradient Maps are often used to create artistic effects like the “posterize” effect, which reduces the number of colors in an image to create a bold, graphic look. You can also use them to create vintage film effects or other creative color styles.
3. Curves: Precision Tone Adjustment
The Curves adjustment layer is the ultimate tool for precise control over the tonal range and contrast of an image. It offers a highly nuanced approach to color manipulation by allowing you to adjust the relationship between the lightness and darkness of pixels.
- The Curves Graph: The Curves window features a graph with horizontal and vertical axes. The horizontal axis represents the input levels (the original pixel values), while the vertical axis represents the output levels (the adjusted pixel values).
- Modifying the Curve: You can add points to the Curves graph and drag them to adjust the relationship between input and output levels. By manipulating the curve, you can control the contrast, brightness, and color balance of your image. For example, an S-shaped curve will enhance the contrast, while a straight line will maintain the original tonality.
- Precision Color Control: You can even use the Curves tool to make selective changes to specific color channels (red, green, or blue), allowing you to fine-tune individual colors in detail.
The Curves adjustment layer is a powerful tool that requires practice and experimentation, but it offers unparalleled flexibility and control over color manipulation in Photoshop. It is a favorite tool among professional photographers and retouchers, allowing them to subtly refine images or achieve dramatic effects.
How To Change A Picture Color In Photoshop
Embracing the Creative Journey: Experimenting with Color
Mastering color manipulation in Photoshop isn’t just about technical knowledge; it’s about becoming a visual artist, taking control of the color palette to express a specific mood, theme, or story. Don’t be afraid to experiment, play with colors, and discover what appeals to your unique vision. Every image holds the potential for transformation, and with the right techniques, you can unveil its full artistic potential, transforming it into something truly special.
The world of color is vast and exciting. Embrace the boundless possibilities, practice these techniques, and watch your creativity flourish as you transform images into captivating works of art. If you’re ready to dive deeper, countless online tutorials and resources can guide you on your creative journey. And remember, color is a powerful tool for communication, storytelling, and emotion. With Photoshop at your disposal, the world of visual expression is your canvas. So, get creative, experiment, and start transforming your images today!”

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




