Have you ever noticed how a black car seems to bake in the sun while a white car stays relatively cool? Or how dark clothing makes you feel hotter in the summer? This isn’t just a feeling; it’s a scientific fact. Darker colors actually absorb more heat than lighter colors, and there’s a fascinating reason behind it.

Image: www.pinterest.com
I remember one particularly hot summer day when I was a kid. My dad, always the practical one, suggested I wear a white shirt instead of my usual black tee. I thought he was being silly, but to my surprise, I actually felt cooler throughout the day. This simple experience sparked my curiosity about why colors could affect temperature so drastically.
Understanding the Science Behind Color and Heat Absorption
The reason why darker colors absorb more heat is related to how they interact with light. Light, as we know, is made up of different wavelengths, each corresponding to a different color. When light strikes an object, it can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted.
Darker colors, like black, absorb nearly all wavelengths of light. This means they convert almost all the light energy into heat energy, causing the object to warm up. On the other hand, lighter colors, like white, reflect most wavelengths of light. They absorb less light energy and therefore generate less heat.
The Role of Pigments and Surface Texture
The specific pigments in a color also influence how much heat it absorbs. For instance, black pigment is often made from carbon, which is an excellent absorber of light. Similarly, dark blue pigments often contain cobalt, another great heat absorber.
The surface texture of an object also plays a role. Smooth, shiny surfaces reflect more light, while rough, matte surfaces absorb more light. This is why a black car with a shiny paint job may heat up less than a black car with a matte finish.
Consequences of Color and Heat Absorption
The phenomenon of darker colors absorbing more heat has several practical consequences. In architecture, for example, buildings with darker roofs tend to get hotter than those with lighter roofs. This is why many modern buildings feature white or light-colored roofs to reduce energy costs associated with cooling.
In clothing, wearing dark colors on a hot day can make you feel significantly warmer. This is because the dark fabric absorbs more sunlight and converts it into heat. Wearing light colors, on the other hand, reflects more sunlight and keeps you cooler.
Even in the natural world, the principle of color and heat absorption plays a vital role. Darker-colored animals, like penguins, are better adapted to cold environments because they absorb more heat from the sun. Conversely, lighter-colored animals, like snow leopards, are better suited for snowy landscapes because they blend in and absorb less heat.
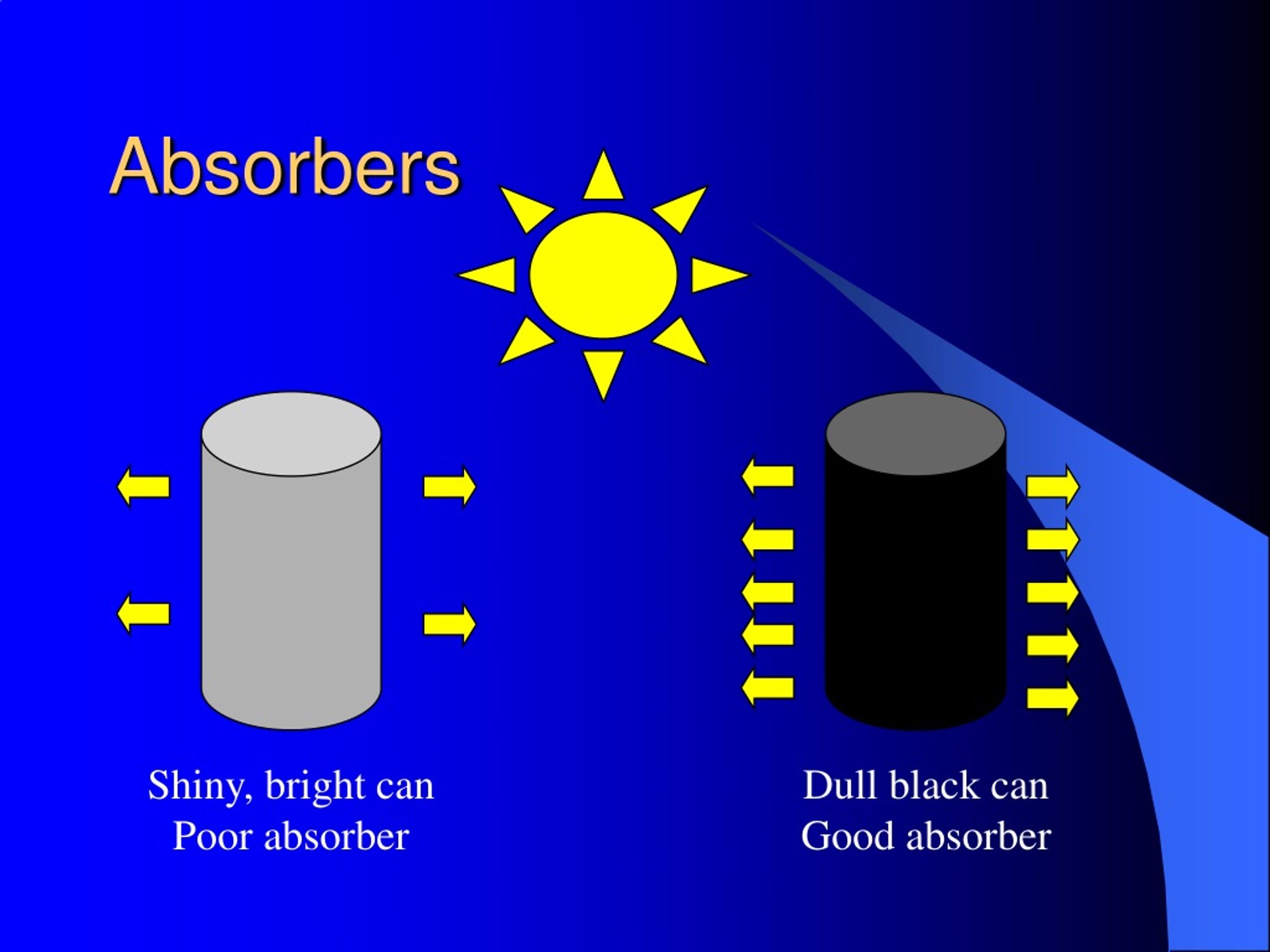
Image: www.slideserve.com
Tips for Managing Heat Absorption
Based on our understanding of how color affects heat absorption, here are some tips for managing temperature in different settings:
- Choose light-colored clothing in hot weather. This helps reflect sunlight and keep you cooler.
- Consider a light-colored roof for your house. This can reduce energy costs associated with cooling.
- Use dark-colored materials for heat-absorbing applications. Consider black or dark-colored materials for solar panels or other applications where heat absorption is desired.
Expert Advice: Maximizing the Benefits of Color
By understanding the science behind color and heat absorption, you can make informed decisions to manage temperature in various aspects of your life. If you live in a hot climate, consider using light-colored paints for your house and choosing light-colored clothing for everyday wear.
If you’re interested in sustainable living, consider incorporating light-colored materials into your home design. For instance, light-colored roofs help reduce the urban heat island effect, which can improve air quality and reduce energy consumption.
FAQs
Why does a black car get hotter than a white car?
Black cars absorb more sunlight and convert it into heat, while white cars reflect more sunlight and generate less heat. This is why black cars tend to get significantly hotter than white cars, especially on sunny days.
Is there any way to make a dark-colored object reflect more light?
Yes, there are ways to modify a dark-colored object to reflect more light. One way is to apply a shiny coating or polish. Another is to change the surface texture to make it smoother, which can increase reflection.
Can color affect the temperature of other things besides objects?
Yes, color can also affect the temperature of things like water and soil. For instance, dark-colored soil absorbs more heat from the sun and reaches a higher temperature than light-colored soil.
Why Do Darker Colors Absorb More Heat
Conclusion
Understanding why darker colors absorb more heat gives us a deeper appreciation for the interplay between light, color, and temperature. By employing thoughtful color choices, we can manage heat absorption in various settings and make more informed decisions about everything from clothing to architecture. This knowledge empowers us to design spaces and products that are both stylish and efficient.
Are you interested in learning more about the science behind color and heat absorption?

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OrangeGloEverydayHardwoodFloorCleaner22oz-5a95a4dd04d1cf0037cbd59c.jpeg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)




